Education in the Russian Federation
Pre-school education in England begins at the age of 3 or 4. Around half of the children at this age attend nursery schools or playgroups mostly organised by parents. Children of this age need care as well as education. That's why kids play a lot, learn to listen attentively and to behave.
Compulsory primary education begins at the age of five in England, Wales and Scotland and at four in Northern Ireland. Children start their school career in an in fant school. Lessons start at
When they are 7 pupils move to a junior school, which lasts four years till they are 11. They study a lot of subjects: English, Mathematics, Science, History, Geography along with Technology, Music, Art and Physical education
Most of children (over 90 per cent) go to state schools where education is free. Only a small proportion of them attend private (Public) or independent schools. Parents have to pay for the education at these schools. The fees are high and only some families can afford it. So such schools are for the representatives of the high class of England. The most notable Public schools are Eton, Harrow, Winchester, Rugby.
Secondary education begins at 11. The majority of secondary schools are Comprehensive schools where boys and girls study together. Besides, parents can take their sons and daughters to Grammar schools or Secondary Modem Schools.
Grammar schools provide an academic course from 11 to 18. They prepare pupils for colleges and universities.
Many children of working class families go to Modern schools- They give a very limited education. Pupils get instruction in woodwork, metalwork, sewing, shorthand, typing and cooking. After finishing such a school a pupil becomes an unskilled worker.
The Comprehensive Schools have their own «Grammar school» classes and «Modern classes»
Every pupil has to choose a set of subjects to learn. If he takes up Art he will study English Literature, Music, Art, Drama and foreign languages. If he is good at exact and natural sciences, he will learn Science: Mathematics, Physics, Chemistry. Biology. Geography, Economics and Technical Drawing.
The British government encourages careers education in the country. That's why secondary schools try to break down the barriers between education and business. They set up close links with firms to allow their students to take part in business activities.
At around 16 years old teenagers take some exams and coursework to get General Certificate of Education. Those who choose to stay on at school usually study for two further years to pass A level (Advanced level) ex-ms. These exams will give them a chance to enter the niversity.
Words
to be aimed to — преследовать цель
pre-school — дошкольное
to attend — посещать
nursery school —
compulsory — обязательный
primary education — начальное образование
infant school — подготовительная школа
junior school — начальная школа
science — естествознание
secondary education — среднее образование
limited — ограниченный
sewing — шитье
shorthand — стенография
unskilled — неквалифицированный
to encourage — поощрять
link — связь
Questions
1) What is a system of education aimed to?
______________________________________________________
Higher education in the USA is not nation-wide. Colleges differ a lot from each other in scale and level of education as well as in the “quality” of diplomas given. There are private and state universities. Private education is considered more prestigious. The most famous private university is Harvard. Higher education is rather expensive in the USA.
A typical American university has two levels of education: two years of undergraduate classes and two more years of graduate classes. The undergraduate years are called the freshman and the sophomore year. During the first and the second year the students take subjects of general education: Science, Humanities, Arts. The specialization begins at the third and the fourth years, named the junior and the senior year respectively. After the fourth year at college, students get a Bachelor’s degree. Graduates may specialize further and do research. They get a Master’s Degree.
EXERCISES 20. Give the English equivalents of the following words and word combinations:
федеральный стандарт образования; учебные и образовательные программы; универсальные требования; начальная школа; средняя школа; считается более престижным; самый известный; довольно дорогое; первый курс; второй курс; третий курс; четвертый курс; общеобразовательные предметы; специализация; степень бакалавра; степень магистра
21. Agree or disagree:
1. The system of education in the USA works according to the national standard.
2. Admission to elementary and high schools is free.
3. State universities are more prestigious than private ones.
4. The course in a typical American university lasts five or six years.
5. Sophomore is the second year in a university.
6. The specialization begins at the first year of studies in a university.
22. Make up ten questions on the text.
23. Compare education in the United States and in Russia.
24. Speak about education in the United States.
_________________________________________________
Education in the USA
Текст на английском языке | Перевод |
The system of education in the United States is rather complicated. | Система образования в США довольно сложна. |
It is exposed to the constant changes of federal policies, adaptation to various social needs, and the emergence of new pedagogical methods. | Она подвержена постоянным изменениям федеральных правил, адаптации к различным нуждам общества и появлению новых педагогических методов. |
In most schools, it is divided into three levels: | Во многих школах образование делится на три уровня: |
elementary school – grades 1 to 5, | Начальная школа — с 1 по 5 класс, |
middle school — grades 6 to 8, | Средняя школа — с 6 по 8 класс, |
high school — grades 9 to 12. | Старшая школа — с 9 по 12 класс. |
This 12-year system is called “K-12”. | Эти 12-летняя система называется «К-12». |
K-12 stands for the grades for students of various age groups from the kindergarten age (5 years old) to the 12th grade age (18 years old). | «К-12» — это классы для студентов различных возрастных групп, от детсадовского возраста (5 лет), до 12 класса (18 лет). |
There are three types of schools in the United States: public, private, and home schools. | В США три типа школ: государственные школы, частные, а также домашнее обучение. |
Public schooling is financed by federal, state, and local authorities. | Государственные школы финансируются федеральными властями, властями штата и местными властями. |
Parents do not pay for their children’s education. | Родители не платят за образование детей. |
Private schools have a right to choose their curriculum and establish their policies. This kind of education is not free of charge. | Частные школы имеют право выбирать свой учебный план и устанавливать свои правила. Такой вид образования не является платным. |
Homeschooling addresses the needs of parents who do not want their children to attend regular schools for certain reasons. | Домашнее обучение удовлетворяет потребность родителей, которые, по определенным причинам, не хотят, чтобы их дети посещали обычные школы. |
Among home school students are children with special needs and children whose parents support non-traditional methods of learning. | К детям на домашнем обучении относятся дети с особыми потребностями и дети, чьи родители поддерживают нетрадиционные методы обучения. |
There are also young athletes and celebrities whose tight schedule do not leave them enough time for going to school. | Также есть юные спортсмены и знаменитости, чей напряженный график не оставляет им времени на то, чтобы ходить в школу. |
About 3% of children are homeschooled in the USA. | Около 3% детей в США находятся на домашнем обучении. |
The necessary standards of education in the United States are set by state governments. | Необходимые стандарты образования в США устанавливаются правительством штата. |
As a rule, the key requirement for American students is to pass obligatory standardized tests developed for the K-12 schooling system. | Как правило, главное требование к американским школьникам — это пройти обязательные стандартизированные тесты, разработанные для 12-летней школьной системы. |
After high school, children have several options. | После старшей школы у детей есть несколько вариантов. |
First, they can choose a 4-year college or university program and get the education for the selected professional career. | Во-первых, они могут выбрать 4-летнюю программу в колледже или университете и получить образование, необходимое для выбранной профессиональной карьеры. |
Second, children can choose a 2-year program in college and get prepared for their future career choice. | Во-вторых, дети могут выбрать 2-летнюю программу в колледже и подготовиться к будущему выбору карьеры. |
Third, high school graduates can enter a vocational school and learn a trade to have an opportunity to be employed in a specific field of occupation such as design, baking or carpentry. | В третьих, выпускники старшей школы могут поступить в профессиональное учебное заведение и изучить профессию, чтобы получить возможность найти работу в определенной обрасти или сфере деятельности, к примеру: профессия пекаря, дизайн, плотническое дело. |
Fourth, graduates of high schools can choose to serve in the US armed forces. | В четвертых, выпускники старшей школы могут выбрать службу в Вооруженных силах США. |
Fifth, if children are not ready to continue their education, they can have a gap year. | В пятых, если дети не готовы продолжать учебу, они могут взять перерыв в один год («gap year»). |
Most kids prefer to spend this time exploring their life preferences and individual interests through active involvement in various jobs, internships, volunteering work, or traveling. | Многие дети предпочитают проводить это время, изучая их жизненные предпочтения и личные интересы через активное участие в различных работах, стажировках, волонтерских программах или путешествиях. |
The primary school divides students into two levels: infants, aged 5-7, and juniors, aged 7-11. At this stage, the major goal is to give children the very basics of education. | В начальной школе ученики делятся на два уровня: «infants» (букв. «малыши») — 5-7 лет, и «juniors» (букв. «младшие») — 7-11 лет. На этом этапе главная цель — дать детям самое основное образование. |
Kids learn to read, write, and do sums. | Дети учатся читать, писать и считать. |
The secondary school differs from the primary school as its program is more complicated. | Средняя школа отличается от начальной, так как ее программа сложнее. |
Several subjects should be studied by all students, including English, Mathematics, Social Sciences, Humanities, and Modern Languages and Literature. | Все ученики должны изучать несколько предметов, включая английский язык, математику, науки об обществе, гуманитарные науки, современные языки и литературу. |
Moreover, there are optional subjects for every student depending on their interests. | Более того, существуют факультативные предметы для учеников, в зависимости от их интересов. |
They include various Arts and Sciences categories of studies. | В их число входят различные дисциплины об искусстве и науке. |
In this country, both free and paid schools are available. | В этой стране доступно как бесплатное, так и платное образование. |
State schools are financed by the government, and students do not pay for their education. | Государственные школы обеспечиваются правительством, и ученики не платят за свое образование. |
Independent schools require parents to pay for their children’s classes. | В частных школах родителям необходимо платить за уроки их детей. |
One can find certain differences in the overall functioning of the system of education in England, Scotland and Wales, because of different schooling policies that affect this scheme. | Можно найти различия в общей работе образовательных систем в Англии, Шотландии и Уэльсе. Причина тому — различия в правилах в области образования, влияющие на эту схему. |
Children should pass a standard exam after high school graduation. | После окончания старших классов дети должны сдать стандартный экзамен. |
The results of the examination will show their eligibility to continue their education in universities. | Результаты экзамена определяют их доступ к продолжению образования в университетах (т. е. показывают, можно им учиться в университетах или нет). |
Further education includes all types of college-level programs and courses chosen by a student after the completion of the period of compulsory education. | Дальнейшее образование включает все типы программ уровня колледжа и курсы, которые ученики выбирают после обязательного периода обучения. |
At this stage, students are offered basic skills training options, and vocational education necessary for employment in a selected occupation. | На этом этапе ученикам предлагают изучать основы различных профессий, профессиональное образование, необходимое для работы в выбранной области. |
Schooling GLOSSARY
1. Kinds of School (Типы учебных заведений):
- primary school – начальная школа
- secondary (high) school – средняя школа
- higher school – высшее учебное заведение
- comprehensive school – общеобразовательная школа
- a school, specializing in — школа, специализирующаяся на
- gymnasium — гимназия
- lyceum – лицей
- technical school — техникум
- college — колледж
- grammar school - средняя классическая школа
- modern school - средняя современная школа без преподавания классических языков (для детей от 11 до 16 лет;государственная)
- technical school - техническая школа (средняя общеобразовательная школа с профессиональным уклоном для учащихся от 11 до 16 или до 18 лет; наиболее успешно сдавшие экзамены имеют право на поступление в вузы)
- comprehensive school - единая средняя школа (государственная;дети принимаются без отборочных экзаменов и обучаются по общей программе до 13-15 лет; затем - по специальной программе в зависимости от наклонностей)
2. Levels of Education
- compulsory education - обязательное обучение
- pre-school education - дошкольное обучение
- primary education - начальное обучение
- secondary education - среднее образование
- higher education - высшее образование
- further education - дальнейшее образование (дневное и вечернее, платное; основная цель - повышение квалификации
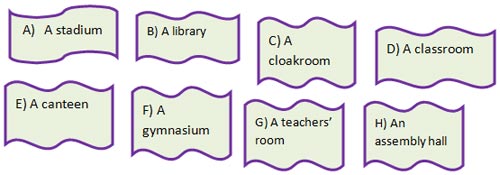
3. School Building & School Interior (Школьное здание снаружи и внутри):
- three-storey building — трехэтажное здание
- classroom — кабинет
- classroom of Russian (= Russian classroom)
- computer classroom – кабинет информатики
- be well-equipped with — хорош-оборудованный
- on the ground (first) floor — на первом этаже
- staff room (teacher’s room)- учительская
- sick room (doctor’s office, medical room) — медпункт
- school office — канцелярия
- canteen – буфет
- dining-hall — столовая в школе
- recreation — рекреация
- cloak-room (changing room) – раздевалка
- assembly hall – актовый зал
- gym- hall (gymnasium ) – спортивный зал
- workshop – мастерская
- headmaster’s office — кабинет директора
- laboratory – лаборатория
- library – библиотека
- entrance hall – вестибюль
- school museum – школьный музей
- diploma — грамота
- poster — плакат
- stand — стенд
4. Staff, Students & Attendance (Персонал, учащиеся и посещаемость):
- headmaster (headmistress) — директор
- director of studies — завуч
- form mistress — классная руководительница
- librarian — библиотекарь
- nurse — медсестра
- security guard — охранник
- pupil — ученик начальной школы
- student — учащийся (ученик средней школы)
- schoolboy — школьник
- junior pupils – ученики младших классов
- senior students –старшеклассники
- attend lessons and classes — посещать уроки и занятия
- enter school — поступить в школу
- leave (finish) school — закончить школу
- pass from …. to….- перейти из….. в….
- miss school — пропускать школу
- change school — поменять школу
5. School Curriculum & School Subjects ( Учебный план и предметы):
- timetable — расписание (on the timetable)
- curriculum — учебный план
- term – четверть
- academic year – учебный год
- at the end of each term… — в конце четверти
- obligatory — обязательный
- optional – факультативный
- lesson of Chemistry = Chemistry lesson — урок химии
- learn (study) different subjects — изучать различные предметы
- advanced mathematics – углубленный курс математики
- Science — точные науки
- The Humanities — предметы гуманитарного цикла
- study Science/ the Humanities — изучать предметы научного / гуманитарного цикла
- attend the optional (elective) class in ….. – необязательный, факультативный
6. Studying at School & School Problems (Учеба в школе и школьные проблемы):
- do well — учиться хорошо
- do badly — учиться плохо
- solve problems in mathematics, physics — решать задачи по математике, физике
- prove theorems — доказывать теоремы
- do equations — решать уравнения
- do experiments in the lab — делать опыты в лаборатории
- swot smth – зубрить
- make smth out – понимать, разбираться в чем-то
- cheat – списывать, пользоваться шпаргалками
- prompt – подсказывать
- work by fits and starts — заниматься урывками
- studies — занятия
- exams — экзамены
- extra lessons — дополнительные занятия
- private lessons — частные уроки
- take lessons — брать уроки
- give lessons — давать уроки
- take an exam in Maths — сдавать экзамен по математике
- fail an exam — провалить экзамен
- pass an exam — сдать экзамен
- weak point — слабое место
- poor memory — плохая память
- can’t remember dates (words, formulas) — не запоминать даты, слова, формулы
- fail to retell texts – не получается пересказывать тексты
- fresher — первокурсник
- sophomore — второкурсник
- junior — младшекурсник
- senior — старшекурсник
- graduator — выпускник
- post-graduate — аспирант
- graduate-school — аспирантура
- to do research / to be engaged in — заниматься научными исследованиями
- scientific advisor / supervisor — научный руководитель
- science — наука
- scientific research — научное исследование
- to investigate — исследовать
- scientist — ученый:
- leading — ведущий
- outstanding -выдающийся
- well-known — хорошо известный
- world- known — всемирно известный
Test 1. School
- They ___________ me a lot at school. (taught, studied, learned)
- I’m ____________my final exam next month. (passing, taking, making)
- “ Have you ________your homework?” Pat’s mother asked her. (made, done, wrote)
- Children have to carry heavy________. (sacks, schoolbags, handbags)
- They have a very good school ____________. (restaurant, bar, canteen)
- _________is my favourite subject. (Historic, History, Story)
- I’m not _______________ Geography and Physics. (well with, good with, good at)
- These pupils are waiting for their teacher in the _________. (classroom, lesson, class)
- Sit ___________your desk and go on with your work. (at, on, near)
- No one likes to _____________ an exam. (lose, fail, fall)
Test 2. School Life
- Who is the ________ of your school? (director, headmaster, chief)
- Clare was very popular with her ________. (schoolfellows, schoolchildren, schoolmates)
- Mathematics is a ______________subject at school. (forced, compulsory, required)
- A___________ is all the different courses that are taught in a school or college. (curriculum, scheme, timetable)
- A __________ is a state school in which children of all abilities study together. (public school, elementary, comprehensive)
- I’m _________English and French classes. (following, attending, visiting)
- A nursery school is for ________. (babies, infants, nurses)
- Every one of their children___________ well at school. (did, succeeded, managed)
- A ________ is a school in Britain for children aged between 11 and 18 who have a high academic ability. (grammar school, state school, special school)
- It’s hard to ___________into the university. (enter, get, go)
- The function of school is to ______________ children. (bring up, educate, encourage)
- We’re building a car at our school ____________ (workshop, laboratory, workplace)
No comments:
Post a Comment